
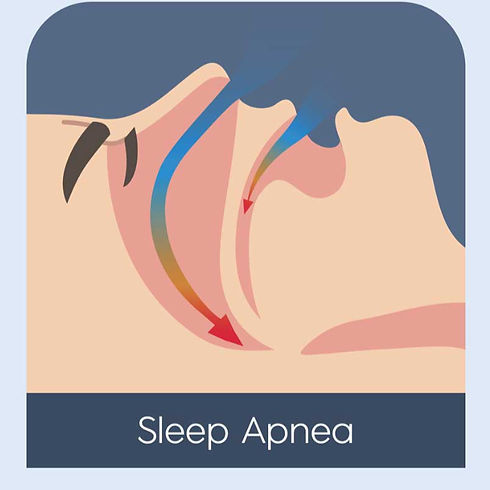
Sleep apnea is a common but serious sleep disorder where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during the night. This can lead to poor sleep quality, daytime fatigue, and increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health problems. The most common type, obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), occurs when the airway becomes blocked during sleep. Many people with sleep apnea go undiagnosed and untreated. Fortunately, with the right solution — including non-invasive therapies — you can breathe easier, sleep better, and live healthier.
Risk
Untreated sleep apnea can have serious long-term health consequences. It increases the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and irregular heart rhythms. It can also lead to chronic fatigue, poor concentration, mood disorders, and even a higher risk of accidents due to daytime drowsiness. Over time, these complications can significantly impact your overall quality of life and increase the likelihood of serious medical events.

Common Signs
Many people live with sleep apnea without knowing it. If you snore loudly, wake up gasping for air, or feel tired even after a full night’s sleep, you may be experiencing sleep apnea. Other common signs include morning headaches, dry mouth, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and frequent nighttime awakenings. If your partner notices you stop breathing during sleep or you often feel drowsy during the day, it’s worth getting checked. These symptoms might seem minor, but they could point to a serious sleep disorder that affects your health and well-being.